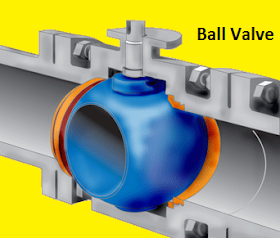
What is a Ball Valve ?
A
ball valve is a rotational motion (quarter turn),quick rotating valve that uses
a ball-shaped disk to stop or start or regulate fluid flow.The function of this type of valves,ball
is same as of disk in globe valve. When the valve handle is turned to open the
valve, the spherical ball rotates to a position where the hole through the ball
is in-line with the valve body inlet and outlet of flow. When the valve is
shut, the ball is rotated so that the
hole is perpendicular to the flow openings of the valve body and the flow is
stopped.
Ball
valve actuators are of the quick-acting type, which require a 90° turn of the
valve handle to operate the valve. Some ball valve actuators such as planetary
gear-operated, allow the use of a
relatively small operating force to operate a fairly large valve.
Some
ball type valves have been developed with a spherical surface coated plug that is
off to one side in the open position and rotates into the flow passage until disk
blocks the flow path completely.
Advantages of
Ball Valves
- A ball valve is the least expensive of any valve arrangement
- Ball valve offers low maintenance costs.
- Ball valves are compact, require no lubrication, and give tight sealing with low torque.
Disadvantages of
Ball Valves
- Ball type valves(especially old designs) have relatively poor throttling characteristics.
- In a throttling position, the partially exposed seat of ball valve rapidly erodes because of the impingement of high velocity flow.
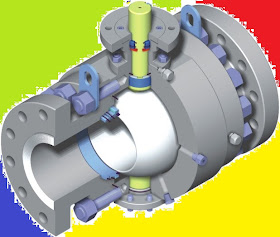 |
| Ball valve |
Valve Materials
in Ball valves
Balls
are usually metallic with trim (seats) produced from elastomeric (like rubber)
materials. Plastic construction in ball valves is also available.
The
resilient seats for ball valves are made from teflon (TFE), filled TFE, Nylon,
Buna-N, Neoprene, other combinations of these materials.Because of these
elastomeric materials ball valves cannot be traditionally used at elevated
temperature and engineer must take care while selecting ball valve for
particular application.
Ball Valve Port
Patterns ,Bonnet & Stem Design
Ball
valves are available in the venturi, reduced, and full port pattern. The full
port
pattern
has a ball with a bore equal to the inside diameter of the pipe.
The
stem and ball connection is explained here.The stem in a ball valve is not
fastened to the ball. It normally has a rectangular portion at the ball end
which fits into a slot cut into the ball. The enlargement permits rotation of
the ball as the stem is turned. A bonnet cap fastens to the body, which holds
the stem assembly and ball in place. Adjustment of the bonnet cap permits
compression of the packing, which supplies the stem seal. Packing for ball
valve stems is usually in the configuration of die-formed packing rings
normally of TFE, TFE-filled, or TFE-impregnated material. Some ball valve stems
are sealed by means of O-rings rather
than packing.
Ball Valve
Positions
Some
ball valves are equipped with stops that permit only 90° rotation. Others do
not have stops and may be rotated 360°. Whether there is stop available or not,
a 90° rotation is all that is required for closing or opening a ball valve.
The handle indicates valve ball
position. When the handle lies along the axis of the valve, the valve is open.
When the handle lies 90° across the axis of the valve, the valve is closed.
Some ball valve stems have a groove cut in the top face of the stem that shows
the flowpath through the ball. Observation of the
groove position indicates the position of the port through the ball. This
feature is particularly advantageous on multiport ball valves.